
The Effects of Stress on the Immune System and How to Protect Yourself
Stress is one of those things everyone comes across in their life, while it is a natural response to challenges, but at times becomes unfavorable because it becomes constant or prolonged. In today’s fast-moving world, this is more common than ever due to work pressures, personal issues, financial burdens, and many more. Our body reacts to the onset of stress with the fight-or-flight mode by releasing hormones, such as cortisol and adrenaline, in an attempt to facilitate our response to danger. Such a reaction may be essential for an acute period but turns harmful if continued over a longer period of time.
Probably, the most crucial impact of chronic stress is on the immune system. The immune system is supposed to fight off invading agents such as bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens from the body. In the event that it becomes chronic, the body loses the ability to combat infections and recover from illnesses. Overproduction of cortisol can compromise the proper functioning of the immune system, hence making the body vulnerable to numerous diseases.
Understanding how it affects the immune system is critical in that it empowers one to take steps that could limit its impact. Of course, this post will deal with the relationship between stress and immune health in further detail, explaining how it can weaken the body’s defenses and the what you can do in your life to ward off such. From changing lifestyles to coping mechanisms in themselves, there are numerous ways that can help in decreasing the levels and boost the immune system to stay fit amidst the four walls of life.
Understand Stress and the Immune System
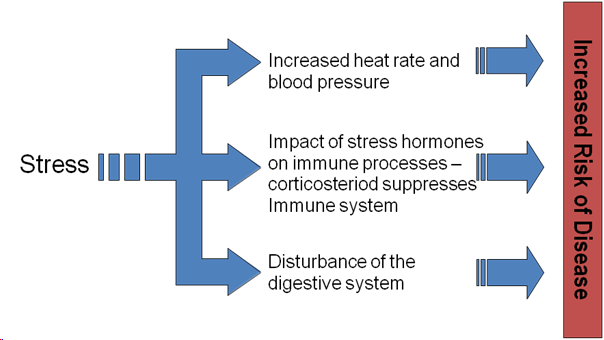
Stress sets a chain reaction in the body. When exposed to a stressor, the hypothalamus within the brain activates the sympathetic nervous system, also known as the fight-or-flight response, which communicates that adrenaline and cortisol (the stress hormone) are released to prepare the body for rapid response: boosting heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose levels.
In the short term, this response can be beneficial, providing you with the energy and focus you need to tackle a challenge. However, when it is chronic, it can cause long-term activation of the stress response, which over time can negatively impact your immune system.

How Chronic Stress Impacts the Immune System
Chronic stress has a significant impact on the immune system by weakening its ability to function properly. When stress is prolonged, the body continuously releases high levels of cortisol, a stress hormone that suppresses immune responses. This suppression reduces the production of essential white blood cells and impairs the function of other immune cells, making the body more vulnerable to infections and illnesses. Additionally, chronic stress can lead to increased inflammation in the body, further disrupting immune function and raising the risk of autoimmune diseases and chronic conditions. Over time, this response can result in a weakened immune system that struggles to protect the body from harmful invaders.
1. Weakened Immune Response
Its immunologic system helps ward off infection and disease by removing harmful invaders, but the chronically stressful states suppress immune activity. For any period during which cortisol stays up, the high levels impede the synthesis of white blood cells and reduce activity by most of the rest of the cells within the immune system, making infections much more possible along with slow healing.
Studies have shown that people under chronic stress are more likely to have frequent colds, flu, or even more severe conditions like autoimmune diseases.
2. Inflammation and Stress
Chronic stress has been shown to activate the inflammation of the body. While inflammation is part of the natural defense mechanism of the body, when it becomes chronic, it causes harm. Increased cortisol levels enhance the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which are molecules that promote inflammation. Chronic inflammation can result in a weakened immune response and may contribute to the onset of chronic conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and arthritis.
3. Weakened Vaccine Response
One of the most direct effects of chronic stress on the immune system is the way in which it hampers the response of the body to vaccines. Several studies have been able to show that individuals under stress may have a lower immune response to vaccines, hence less effective at preventing illness. The reason for this is that hormones associated with stress depress the activity of T-cells, which fight off infections and diseases.
4. Increased Risk of Autoimmune Diseases
Chronic stress has been associated with an increased risk of autoimmune diseases, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s tissues. Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis have been associated with long-term stress, as prolonged activation of the stress response can lead to an overactive immune system, causing it to turn against the body.
5. Sleep Disruption and Immune Health
Stress usually results in sleep disorders, for instance, insomnia or patterns of interrupted sleep. This means poor quality sleep additionally undermines the immune system. While asleep, the body repairs and rebuilds cells, including even those cells of the immune system. Chronic deprivation from sleep starts causing the reduction in the production of cytokines, which are proteins considered to play a role in the regulation of the immune responses. The body, therefore, finds it difficult to combat infections.
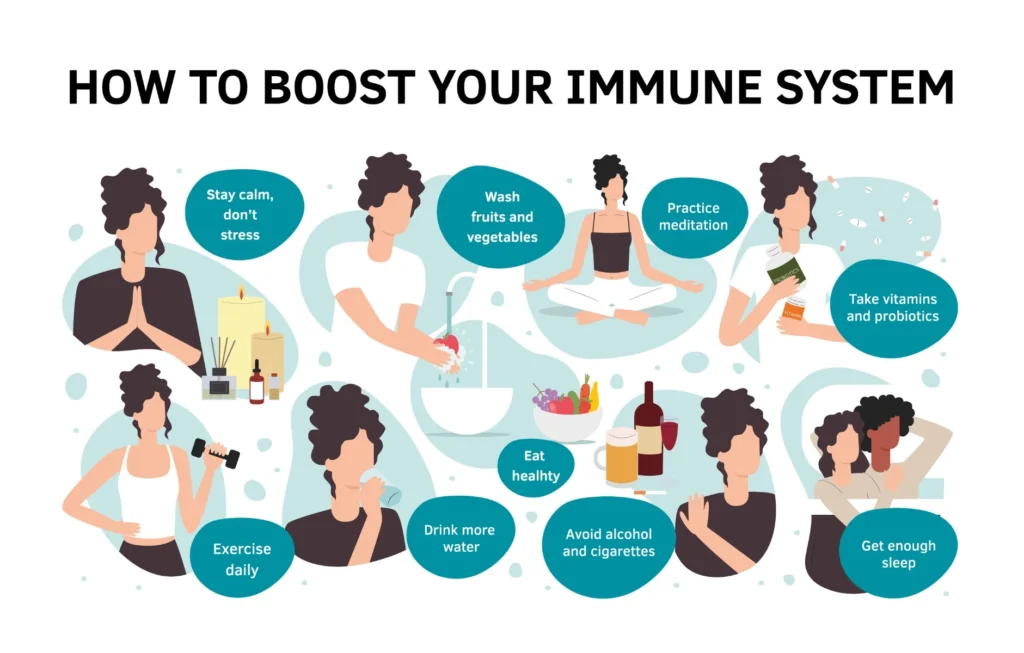
How to Protect Your Immune System from Stress
While it’s impossible to eliminate all stress from your life, there are several ways to protect your immune system and manage stress effectively. Here are some practical steps to reduce stress and maintain a healthy immune system:
1. Exercise Regularly
One of the best coping agents against stress is physical activity. It helps in the release of endorphins, which are natural mood elevators in the body, thereby decreasing the level of stress and generally improving one’s well-being. Regular physical activity also boosts the immune system by increasing the flow of cells that facilitate the ability of the body to fight off infections.
Attempt at least 30 minutes of moderate activity most days a week. There is walking, jogging, yoga, swimming, or several other forms to reduce stress levels and enhance your immune system.
2. Learn Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Mindfulness practice in daily life significantly reduces stress and its negative effects on the immune system. Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, and progressive muscle relaxation activate the parasympathetic nervous system of the body, which acts as a counterbalance to the stress response and induces relaxation.
Spending even as little as 10-15 minutes each day doing mindfulness activities lowers cortisol and raises immune function. Guided meditations are easily found in the apps Headspace or Calm, to get beginners started.
3. Sleep Sufficiently
Quality sleep is essential for maintaining a healthy immune system. Aim for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep each night to allow your body to rest, repair, and regenerate. Creating a relaxing bedtime routine, reducing caffeine intake, and limiting screen time before bed can help improve sleep quality and reduce the negative impact of stress.
4. Maintain a Healthy Diet
A well-balanced diet is critical to immune health. A diet consisting of a variety of whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, will provide the necessary nutrients to support the immune system. Foods rich in vitamins C and D, zinc, and antioxidants can help strengthen the body’s defenses and reduce inflammation.
5. Connect with Others
Social support can play a huge role in minimizing stress and enhancing immunity. You could hang out with friends, spend time with your family, or engage in some group activities, which can really help you relax and feel supported. If you’re feeling overwhelmed, talking to a trusted friend or therapist can help you work through stress and gain perspective.
6. Seek Professional Help
If stress seems to be becoming too much for you or affects your daily activities, consult a mental health practitioner. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), talk therapy, or counseling may help you devise ways to handle stress and lessen its impact on your body.
7. Avoid or reduce caffeine and alcohol
While caffeine and alcohol may give temporary relief from stress, they can also disturb sleep and cause increased levels of stress in the long run. Try to limit your consumption of caffeinated drinks and alcoholic beverages, especially in the evening, to enhance better sleep and health.
Conclusion
Stress in life is inevitable, but chronic stress can be very dire and have a potential impact on your immune system and health. When you understand how it affects the body, you can learn healthy ways of managing stress in a bid to protect your immune system and enhance your ability to overcome life’s turmoil.
Remember, taking daily small steps to reduce stress, such as exercise, healthy eating, and mindfulness, will help your immune system become stronger and allow you to stay healthy for a long time. Therefore, self-care with professional help when needed will not be in vain.




Leave a Reply